Method Statement for Shoring
1.0 Scope
Shoring Method Statement covers design and implementation of Shoring Structure to support loose soil during excavation works.
2.0 Definition
Project : Construction of SARA SKILL Civil Project
Owner/Client : SARA SKILL
Contractor : Approved Contractor by SARA SKILL
SM : Site Manager
CM : Construction Manager
QCM : Quality Control Manager
QCI : QC Inspector
HSEM : Health, Safety and Environment Manager
3.0 Reference and Standards
- Project Specification – Civil/Structural detailed design criteria
- SARA SKILL guidelines specification for construction progress
- IFC Drawing
- ACI - American Concrete Institute
- RC - Royal Commission Standard
- SAES - Saudi Aramco Engineering Standard
- AISC - American Institute of Steel Construction
- ASCE - American Society of Civil Engineers
- OSHA - Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- HCIS - High Commission for Industrial Security
- Safety and Fire Protection Directives for Industrial Facilities
4.0 Purpose
This document will explain the activities and sequence that will take place for shoring works.
5.0 Responsibilities of Contractor
5.1 Site Manager
Site manager will be responsible for the overall direction, coordination, and control of the shoring activities. To assure that work is completed efficiently and in compliance with project specifications.
5.2 Construction Manager
Construction Manager will report to and receive technical direction from the Site Manager. He will be responsible for the overall implementation and monitoring of all the activities. Deal with site supervisor’s team for implementing the Shoring Work in correct procedure at site.
5.3 Quality Control manager
Responsible for overall Quality Control of all construction activities on site. Implementing and monitoring the approved Inspection and Test Plan & procedures for effective results.
5.4 HSE Manager
Safety manager will oversee and enforce the safety regulations and ensure that all personnel involved in the work abide. He will prepare the work safety plan that must be implemented, and safety awareness of personnel involved in the survey works, prior to commence of work.
5.5 HSE Officer
Before starting the work, double-check that all clearance certificates and work permits are issued. Check for compliance with safety regulations such as personal protective equipment (PPE). Check the work environment for any potentially hazardous situations. As per the site HSE plan/procedure, Job Safety Analysis (JSA) shall be strictly implemented before and during survey work.
5.6 Site Supervisor
Site supervisor will report to and review project direction from Construction Manager. He will be directly involved in the planning and execution of the activities in shoring works.
5.7 QC Inspector
QC inspector will ensure that all work carried out as per specification and standard, to report inspection result to Quality manager.
5.8 Foreman
Foreman will be responsible for the direct execution of works involve in the shoring works according to the plan and shall directly control and give instruction to the work personnel. He will also ensure that the works are done with outmost regard to Safety and Quality.
6.0 Location
Sara Skill Project Area
7.0 Equipment, Tools & Manpower
7.1 Equipment
- Hydraulic Crane (if required)
- Hammering machine
- Gas Cutter & Welding Machine
- Dump Truck
- Vibro Hammer
7.2 Tools
- Timber lagging Beams
- Crawler Chain
- Wire Slings
- Hand Tools (Mechanical)
- Hand Shovel
- Surveying Equipment
- Measuring Tape
- Sheet piles
7.2 Manpower
- Site Engineer - 1
- Safety officer - 1
- Site Supervisor - 1
- Foreman - 1
- Equipment operator - 4
- Standby man - 1
- Flagmen - 2
- Skilled worker - 2
- Surveyor - 1
- Helper - 10
8.0 Design Consideration
8.1 Safety
Design shall be placed the first priority on safety. OSHA codes, as well as MARAFIQ/MASA Standards, provide stringent performance specifications regarding Shoring.
8.2 Cost
Shoring structures can be the most expensive part of construction projects. Designing cost- effective solutions to Shoring structures problems could easily be the competitive advantage. The designer shall have a thorough knowledge of all the options which will sufficiently solve the temporary structures problem.
8.3 Unique Design Challenges
Shoring is subject to unique loading conditions which do not apply to a permanent structure (fluctuating or dynamic loads, impact loads, and loads which change position). Working with limited space and crowded sites required the most efficient temporary structure so that personnel can safely maneuver.
9.0 Structural Design
9.1 Responsibility
The structural engineer is responsible for structural design of the Shoring.
9.1.1 Important factors in design
- Safety (the structure doesn’t fall down);
- Serviceability
- Economy (an efficient use of materials and labour)
9.1.2 Types of load that structures support
- Dead loads –is permanent; including self-weight, floor covering, suspended ceiling, partitions, etc.
- Live loads – It is variable as location of furniture, equipment, and building occupants is not fixed.
- Wind load - It Develop a pressure or suction on the outer part of a building.
- Earthquake loads - The effects of ground motion are simulated by a system of horizontal forces.
- Snow load - It varies with geographical location and drift.
- Other loads - It includes hydrostatic pressure and soil pressure. If the load is applied suddenly, the effects of IMPACT must be accounted.
10.0 Shoring Design
When the material for Shoring has been chosen, and the anticipated loading estimated, a form shall be designed strong enough to carry the anticipated loads safely, and stiff enough to hold its shape under full load. Before Shoring design can properly begin, a thorough evaluation shall be made concerning the variables surrounding the design. Some of these include the following:
10.1 Review the Job Conditions
10.1.1 Type of placement procedure.
10.1.2 Deflection tolerances permitted
10.1.3 Access to placement area
10.2 Review Workers Knowledge Level
10.2.1 Expected degree of compliance to design assumptions.
10.3 Establish which Materials will be utilized in the Shoring system
10.3.1 Solider Pile (sizes and allowable stresses) in inventory or readily available
10.3.2 Lumber/Timber Lagging (sizes and allowable stresses) in inventory or readily available
10.3.3 Hardware available (the hardware may dictate the lumber selected for the shoring)
11.0 Work Procedure
11.1 Pre-Requirements
Contractor have to get all necessary work permits from the Client's HSE department prior to starting work. Contractor shall obtain for his staff / workers, equipment, all necessary ID’s and stickers by coordination with client representative for the successful execution of job.
11.2 Survey works
Verify the boundaries of area location according to the drawings issued from the Client before the commencement. Mark the location and limits of the area to be excavated. At all times, all markers must be "flagged" off. Surveyor shall mark the shoring layout.
11.3 Methodology for Shoring
- Prior to beginning of works, the working platform on site shall be prepared. Any debris, vegetation etc. on the ground have to be removed and a reasonably flat and firm working platform has to be obtained for heavy cranes,
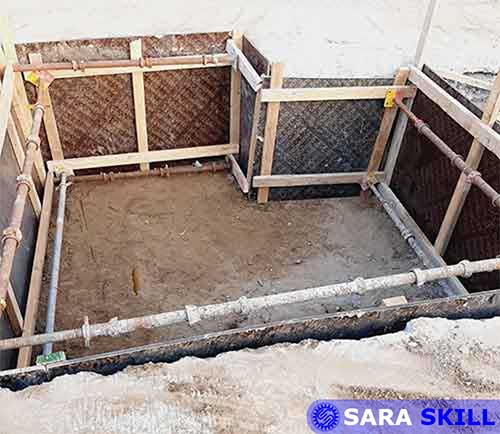
- Once a suitable platform is ready, steel H-beams are installed along the shoring line. H- Beams are installed either by pre-drilling holes or by driving if subsoil conditions permit,
- Excavation is started in the areas in front of the already installed H-beams and carried down to final excavation level / the first anchor level.
- During excavation, timber lagging is placed on exposed excavation face and the volume between the lagging and excavated soil surface is backfilled with suitable granular material.
- Note: Bracing shall be provided wherever it is necessary for the shoring system.

12.0 Safety
Safety of the personnel and properties is to be given prime importance and all the works to be carried out without causing any accidents or property damages. Shoring involves the following activities,
- Storage
- Transportation
- Fabricating & Fixing
- Lifting of Shoring at site
- Removing of Shoring
Access and egress for work site must be provided. All site personnel should be outfitted with the basic personal protective equipment. All the equipments, tools and tackles being used for the work should be in good working conditions and maintained. All the personnel will be provided with toolbox talk on the procedure to execute the work safely.
13.0 Environmental Issues
- Environmental spill kits will be available for use at the work location.
- Other specific measures will be utilized as may be appropriate.
- All instructions given by the banksman must be followed and works cease as appropriate.
- If Cathode protection is required to the steel casing pipe, this will be provided by a specialist contractor and specific method statements will be provided.
14.0 Cleaning
- At the end of each work day, removed unused materials, debris and containers from the site.
- Remove empty bags, cans, pails and other discarded materials.
*************************************